
Understanding SMTP, POP, IMAP & Handling Email Client Issues
1.0 Introduction
This article provides an overview of POP, IMAP, and SMTP are the three main protocols used by email applications to communicate with the email server. These protocols help mail clients retrieve and send messages. A mail client refers to the application users open to manage their emails, such as Outlook, Apple Mail, and Gmail App, or the default mail app on mobile devices. Understanding how these protocols work is important for helping clients. The article explains the differences between POP and IMAP, how SMTP handles outgoing email, and how these protocols affect a user’s email experience. It also outlines the steps staff can follow when clients face issues with email applications such as Outlook, including how to verify that our email server is functioning normally. In addition, this article provides guidance on assisting clients who wish to add their email accounts to Gmail.
2.0 What Are SMTP, POP, IMAP and How do they works ?
SMTP, POP, and IMAP are email protocols, which are the methods that mail clients use to communicate with the email server. They are not email applications themselves instead, they allow applications like Outlook, Apple Mail, Thunderbird, or the Gmail App to send, receive, and manage emails.
2.1 SMTP
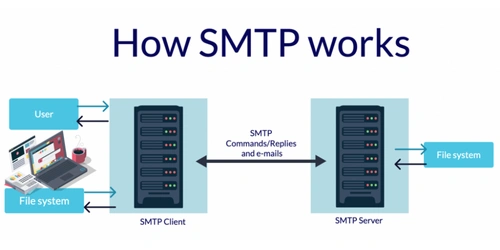
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, and it is responsible for sending email messages. This protocol is used by email clients and mail servers to exchange emails between computers. A mail client communicates with the SMTP server through a specific email port, using SMTP commands and responses to handle outgoing messages. Because of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, emails can be sent from the same account across different email applications.
2.2 POP
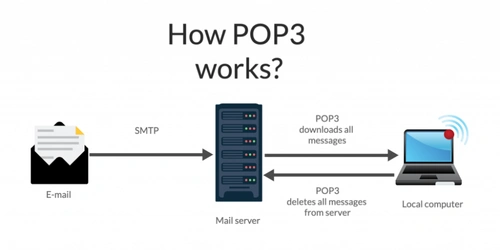
POP, or Post Office Protocol, is a protocol used by mail clients to retrieve emails from the server. When the POP client connects, it downloads all messages from the inbox and saves them to the user’s computer. After downloading, the messages are usually deleted from the server. Because the emails are stored locally, users can continue reading them even without an internet connection.
2.2 IMAP
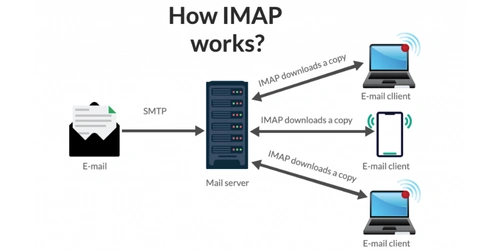
The Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) allows users to access and manage their email messages directly on the mail server. With IMAP, users can organize emails into folders, delete messages, search through their mailbox efficiently, and set or remove email flags. IMAP also supports retrieving specific parts of an email when needed.
By default, all messages remain stored on the server until the user chooses to delete them. IMAP also allows the same mailbox to be accessed from multiple devices, making it suitable for users who need consistent email synchronization across different platforms.
3.0 Troubleshooting Steps for Outlook Email Issues
When a client says that Outlook cannot send or receive emails, follow these steps to identify whether the issue is caused by Outlook or by the email server.
Step 1: Ask the Client to Log In to Webmail
Before checking Outlook, confirm whether the email account itself is working.
- If the client cannot log in to webmail, the issue may be due to an incorrect password or account problem.
- If the client can log in successfully, the email account is active and functioning.
Step 2: Test Sending and Receiving Email Through Webmail
Ask the client to perform two quick tests in webmail
- Send an email to any external address.
- Reply back or send an email to themselves.
If both tests work, this confirms:
- The server is working normally
- Sending and receiving functions are functioning well
If webmail is working, the problem is not related to the server, but to Outlook specifically.
Step 3: Check the Outlook Account Settings
Verify the following information with the client:
- Correct incoming server (IMAP/POP)
- Correct outgoing server (SMTP)
- Correct port numbers
- SSL/TLS security enabled
- Correct email address and password
Many Outlook issues come from incorrect settings.
Step 4: Check Outlook Application and Device Issues
If the settings are correct, the issue may be caused by Outlook or the device. Common issues include:
- Outlook not updated
- Slow or unstable internet connection
- Windows not updated
If the issue comes from Outlook or the client’s device, it is outside the server’s responsibility.
Step 5: Get Support from Outlook
If Webmail is working and all server settings are correct, but Outlook is still having problems, then the issue is caused by the Outlook application or the client’s device. In this situation, staff should advise the client to contact Outlook support or their internal IT team for further help. This ensures the client receives proper assistance while confirming that our email server is functioning normally.
4.0 How to add Webmail to Gmail
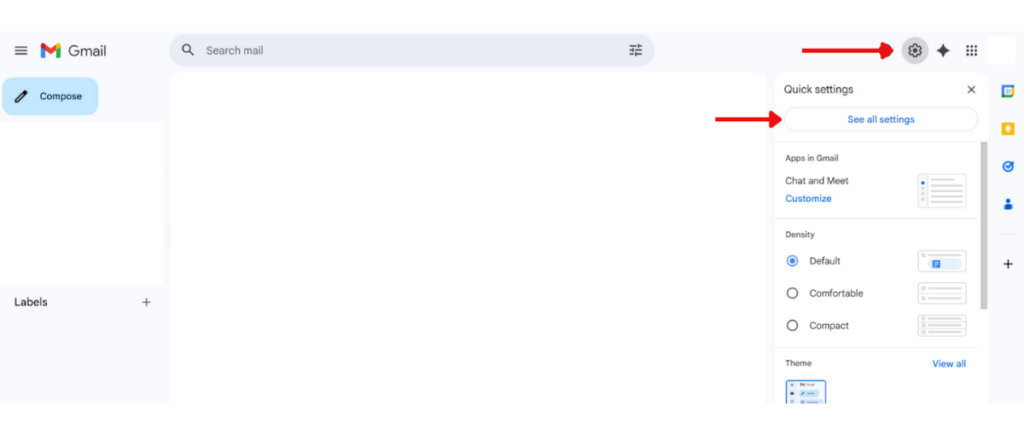
- Sign in to Gmail (mail.google.com) with the user’s Gmail account.
- Click Settings (gear icon), then See all settings.
3. Go to the Accounts and Import tab.
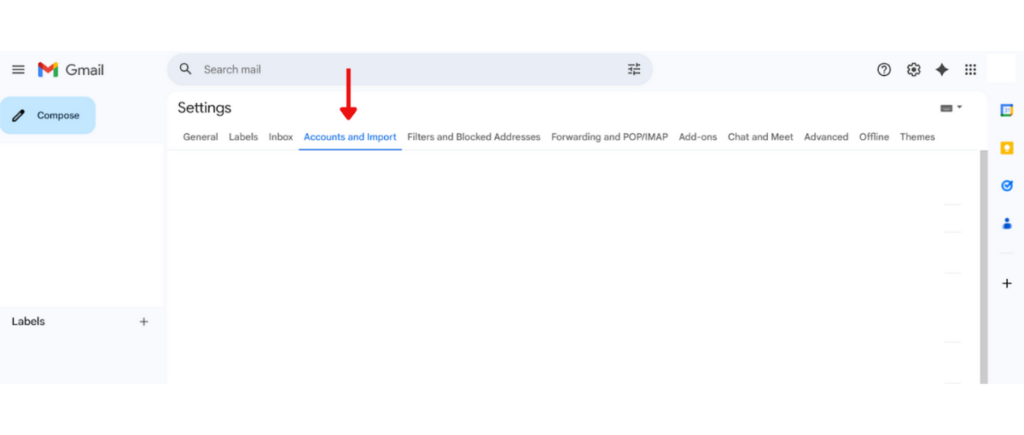
4. Under Send mail as, click Add another email address.
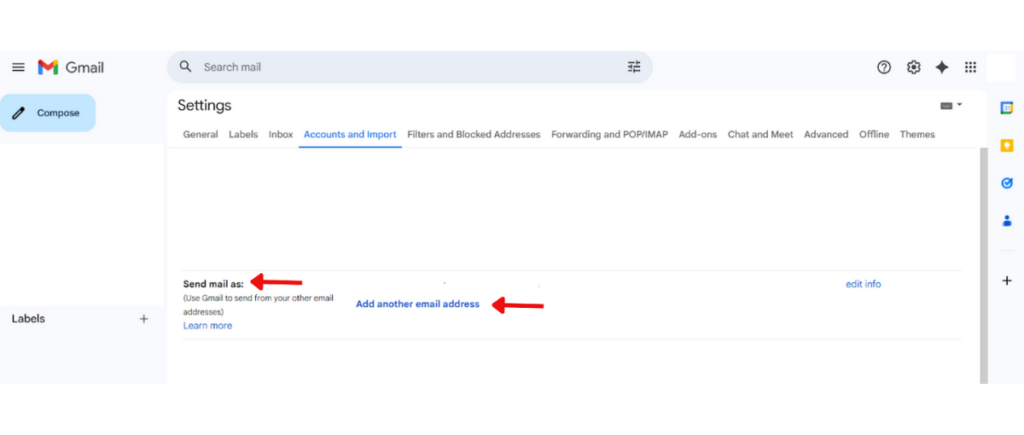
5. In the popup, enter the user’s name at the Name field and the webmail email address at Email address field (example: user@yourdomain.com), then click Next Step.
6. Enter the SMTP settings requested by Gmail:
- SMTP Server: mail.yourdomain.com (replace with user’s SMTP server)
- Port: 465 (SSL) or 587 (TLS)
- Username: Webmail Email Address
- Password: Webmail Password
- Secured connection using SSL (or TLS if port 587), then Click Add Account
7. Gmail will send a verification email to the Webmail Address. Ask the user to open Webmail (or the mail client) and find the verification message. Click the verification link or copy the verification link and paste it to the new browser to confirm.
8. After verification, users can select the webmail address in the From field when composing messages in Gmail.
